An engine is a machine that converts fuel, heat, or other forms of energy into mechanical work to produce motion. All types of engines work by burning some type of fuel. There are various types of engines that can be used in a car.
Internal Combustion Engine is the most common type of engine used in cars & other vehicles. In this type of engine the combustion or burning process takes place inside a cylinder. fuel (usually petrol or diesel) is mixed with air, compressed inside a cylinder, and ignited by a spark or compression, creating a controlled explosion that drives the engine’s pistons and generates power.
Construction of a Car Engine
A car engine is a complex machine made up of several components working together harmoniously. Here’s a brief overview of some key parts:
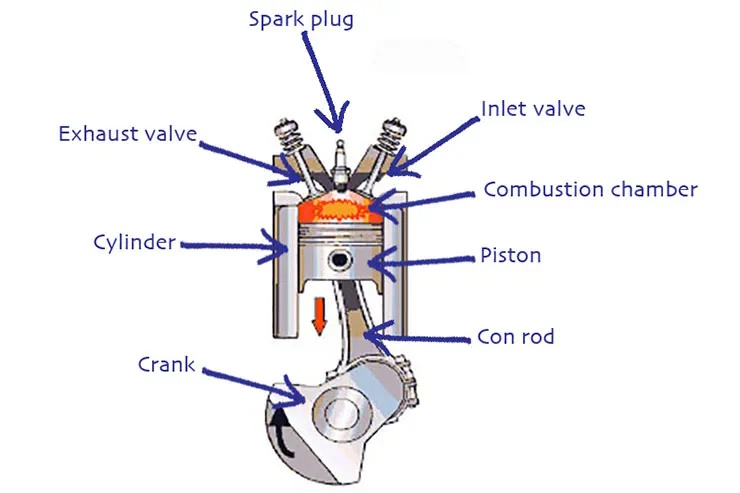
- Cylinder Block: This is the main structure of the engine, housing the cylinders where the magic happens.
- Pistons: These are cylindrical components that move up and down inside the cylinders. They play a crucial role in converting the energy generated by the combustion process into mechanical motion.
- Cylinder Head: Positioned on top of the cylinder block, the cylinder head contains valves and spark plugs, which are essential for the engine’s operation.
- Valves: These are openings that allow air and fuel to enter the cylinders and let exhaust gases escape after combustion.
- Spark Plugs: They ignite the air-fuel mixture inside the cylinders, initiating the combustion process.
- Crankshaft: This is a long, rotating shaft located beneath the cylinders. It converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which ultimately drives the wheels.
How an Engine Works
The operation of a car engine revolves around the concept of internal combustion—a process wherein fuel and air are ignited within the cylinders to produce energy. The process can be broken down into four main stages: suction, compression, power, and exhaust. Let’s explore each stage:
Suction: The engine cycle begins with the intake stroke. During this stage, the piston moves downwards, creating a vacuum inside the cylinder. Simultaneously, the intake valve opens, allowing a mixture of air and fuel to enter the cylinder from the intake manifold. This process is crucial for ensuring the proper air-fuel ratio necessary for combustion.
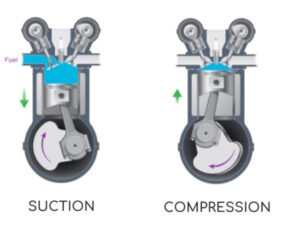
Compression: Once the cylinder is filled with the air-fuel mixture, the intake valve closes, and the piston begins to move back up. As it moves upward, it compresses the air-fuel mixture into a smaller space. This compression increases the pressure and temperature inside the cylinder, preparing the mixture for combustion.
Power: When the piston reaches the top of its stroke, the spark plug generates a spark, igniting the compressed air-fuel mixture. This ignition causes a rapid expansion of gases, creating a powerful force that pushes the piston back down. As the piston moves downward, it transfers its energy to the crankshaft, which rotates to produce mechanical power. This stage is where the engine generates the power needed to propel the vehicle forward.
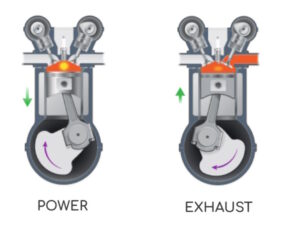
Exhaust: Once the power stroke is complete, the exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves back up again. As it moves upward, it pushes the burned gases out of the cylinder and into the exhaust manifold. From there, the gases travel through the exhaust system and exit the vehicle through the tailpipe. This stage completes the engine cycle and prepares the cylinder for the next intake stroke.
Together, these stages work in harmony to harness the energy of combustion and propel the vehicle forward.